Hypoglycemia refers to low blood sugar or glucose reading in the blood. The severity of its symptoms may seem like diseases but it is not. Hypoglycemia is a sign of an underlying health problem.
Most of the time, this condition occurs in medication dependent diabetic patients. Patients taking oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin-dependent patients are at risk for hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia may also occur in people without diabetes, as well. It may be due to the sudden decrease in food intake or excessive use of energy.
Fortunately for some, having candies, eating, or drinking juice can provide a quick-fix, but this does not apply in all situations.
The normal capillary blood glucose (CBG) is 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Getting a result lower than 80mg/dl is considered as hypoglycemia.
Factors causing hypoglycemia
- Overdose of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents
- Omission of meals or too little food intake
- Strenuous activities or excessive workout
- Gastrointestinal discomforts such as nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Alcohol intake
- Poorly designed insulin regimen
- Lipodystrophy at the injection site – decreased absorption of insulin when injected
- Malabsorption e.g. celiac disease
- Unrecognized other endocrine disorder e.g.addisons
- Breastfeeding by diabetic mother
Symptoms
CBG levels below 80 mg/dL. Some people may feel the symptoms below.
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Feeling shaky
- Hunger
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Palpitations
- Pounding heart; racing pulse
- Pale skin
- Profuse sweating
- Trembling or tremors
- Drowsiness
- Memory lapse
- Muscle weakness
- Anxiety
For severe hypoglycemia, levels below 50 mg/dL affect brain function. The patient may experience the following symptoms, including:
- Poor coordination
- Slurred speech
- Poor concentration
- Blurring of vision
- Numbness in mouth and tongue
- Muscle numbness
- Passing out
- Seizures
- Nightmares or bad dreams
- Coma
Note: Stroke patients also mimic some of the symptoms.
Diagnostics
- Blood glucose level
- Electrolyte levels
Prevention of hypoglycemia
- Advise patient to avoid alcoholic drinks with anti-hyperglycemic medications
- Explain to the patient the different drug interactions with anti-hyperglycemic medications. The following medications have causes drug-related hypoglycemia: instruct not to take allopurinol, aspirin, probenecid, or warfarin with diabetes medications.
- Instruct the patient to monitor blood sugar regularly.
- Familiarize the patients and their relatives with the common signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
- Emphasize the benefits of eating right and on time. Explain the need to eat carbohydrate-rich food before exercising.
- If your patient has a history of hypoglycemia, advice the patients to be ready with candies or chocolates in case of symptoms appear.
Dr. Eric Berg is a chiropractor who specializes in weight loss through nutritional and natural methods. Dr. Berg posted a series of vlogs on hypoglycemia. He states that it is not advisable to treat hypoglycemia with candies because it worsens the condition due to the cycle of hyper-hypoglycemia. A long term solution which is a change in the diet is much more appropriate. In his video, he also discussed that an increase the protein intake with carbohydrates and vegetables can promote a longer goal to prevent hypoglycemia.
Patient Goals
- Disturbed thought process
The patient will…
- Recognize changes in thinking/ behavior
- Verbalize understanding of causative factors when able
- Identify interventions to deal effectively with the situation
- Demonstrate behaviors/ lifestyle changes to prevent/minimize changes in orientation
- Maintain usual reality orientation
- Risk for unstable blood glucose
The patient will…
- Acknowledge factors that may lead to unstable blood glucose
- Verbalize understanding of body and energy needs
- Verbalize plan for modifying factors to prevent/minimize shifts in glucose level
- Maintain glucose in a satisfactory range
Nursing Intervention
- Assess causative or contributing factors by identifying the factors present.
- Assess the degree of impairment.
- Check the current blood glucose.
- For conscious patients with blood glucose is below 60mg/dl give at least 10-15g of fast-acting simple carbohydrates such as 1 tablespoon of honey, 6 pcs of crackers, half glass of juice, or soda.
- For unconscious patients and patients unable to swallow administer dextrose 50% 50ml bolus per IV as prescribed.
- Repeat the patient’s blood glucose level after 1 hour.
- Monitors patient’s vital signs.
- Draw blood for baseline electrolytes.
- Obtain a complete patient history including the last alcohol intake and medications.
Step by Step Treatment of Adult Hypoglycemia Diagram
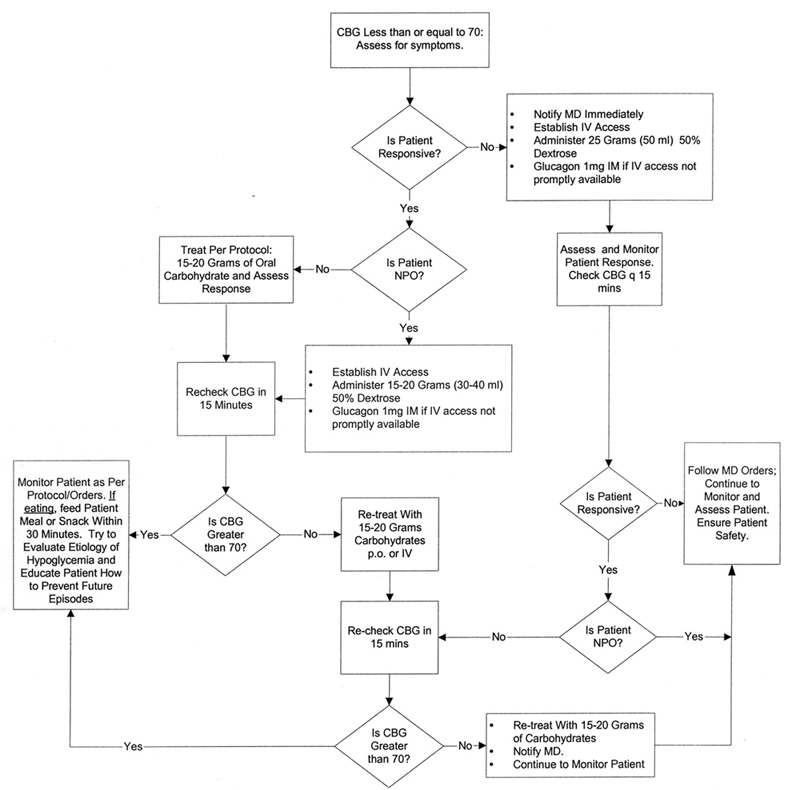
Hypoglycemia is a symptom that can be prevented. Knowing the risk factors, emergency treatment protocols, and guided medication intake. Learn by heart the hypoglycemia signs and symptoms with the patient and his relatives. Early detection and fast and accurate treatment and prevention would ensure optimum health for the patient now and in the future.
References:
- medicinenet.com
- emedicinehealth.com
- medicalnewstoday.com








